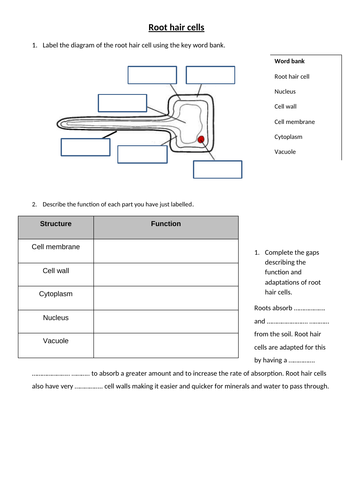
Root hair diagram labeled 450454-Root hair cell labeled diagram
Root Anatomy and Poiseuille's Law for Water Flow in Roots MB Kirkham, in Principles of Soil and Plant Water Relations, 05 B Root Hairs Root hairs appear when the epidermis differentiates The epidermis has specialized cells that are root hair cells Much attention has been given to root hairs because of their presumed importance as absorbing surfaces The epidermis is usually(iii) Draw a labeled diagram of the root hair cell as it would appear if some fertilizer is added to the soil close to it (iv) Name the process responsible for the entry of water molecules from the soil into A1 and then (v) What pressure is responsible for the movement of water in the direction indicated by arrows ?Diagram of an anagen follicle Anagen Growth stage of hair follicle cycle Catagen Regression and involution stage of hair follicle cycle Telogen Resting stage of hair follicle cycle Exogen Active hair shaft shedding stage of hair follicle cycle Kenogen Telogen follicle without club hair form Club hair Fully keratinized, dead hair formed at telogen stage Lanugo hair Fine hairs on the fetus body
Root Hair Cells Adaptations Teaching Resources
Root hair cell labeled diagram
Root hair cell labeled diagram-Hair Diagram A hair grows from the papilla and with the exception of that point of generation is made up of dead, cornified cells It consists of a shaft that projects above the skin, and a root that is imbedded in the skin Figure 2 diagrams how the lower end of the root expands to form the root bulb Its basic components are keratin (a protein), melanin (a pigment), and trace quantities ofName the root system found in mustard plant State the function of root hair



The Diagram Below Represents A Layer Of Epidermal Cells Showing A Fully Grown Root Hair Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
label structure of root cells The shape helps the root hair cell to move around the body, the nucleus helps the root hair cell, the root hair cell is about the same shape as a nerve cell Root hairs are long tubular out growths made of root epidermis cells that form to increase the root surface Root hair development consists of root hair initiation and tip growthRoot hair cells The root hairs are where most water absorption happens They are long and thin so they can penetrate between soil particles and they have
Root hairs greatly increase the surface area of the root, and thereby improve the absorption of water and minerals Root hairs are located about 1/2 inch from the root cap Each root hair is an individual cell Root hairs live for only a few days and never develop into multicell roots Because of their short life, roots need to grow continually CROSS SECTION OF A ROOT A cross sectional Dra A Full Labeled Diagram Of An Epidermal Cell With Chegg Com Solved Ve Ds E Ele 4 The Diagram Alongside Represents A Layer Of Epidermal Cells Showing A Fully Grown Root Hair Study The Diagram And Answer The Questions That Follow A Name 1 The Diagram Below Represents A Layer Of Epidermalcells Showing A Fully Grown Root Hair Study Brainly In Root Hair Cell Labelled angelo Human Heart Anatomy Vector Diagram Etsy In 21 Human Cell Diagram Cell Diagram Human Cell Structure Skin Diagram And Information About Your Skin Integumentary System Skin Anatomy Psoriasis Skin Xerophytic Leaf C S Epidermis Plants Leaves
A look at the structure and function of the root hair cell an example of a specialised plant cell This clip is from Key Stage Three Bitesize Revision First broadcast 29 March 01 Classroom Root hairs are an extension of the root While the root is a complex multicellular organism, root hairs are very small, singlecelled, and only extend out just a few millimeters from the rootRoot hair cell collecting mineral nutrients and water from soil, biological labeled plant system diagram Vector illustration educational cross section




Labelling A Root Hair Cell Diagram Quizlet



Bil 226 Lecture Six
The drawing shows part of a root hair cell (a) Use words from the list to label the parts of the root hair cell cell membrane cell wall cytoplasm nucleus vacuole (4) (b) The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell The dots show the concentration of molecules The cell is respiring aerobically Which arrow, A, B, C or D represents (i) movement of oxygenThe rootsystem in hydrophytes is feebly evolved and root hairs and root cap are absent In some floating plants such as Utricularia, Ceratophyllum, etc, no roots are evolved, and in submerged plants such as Vallisneria, Hydrilla, etc, water dissolved mineral salts and gases are absorbed by their whole surfaceA pie slice diagram shows the proportion of water to typical chemical Hence giving these nerve and muscle cells have the ability to move (a) use words from the list to label the parts of the root hair cell The diagram shows a group of muscle cells from the wall of the intestine Long, tapered muscle cells have an intrinsic stretchiness that




Vector Art Vascular Plant Biological Structure Labeled Diagram Vector Illustration Clipart Drawing Gg Gograph
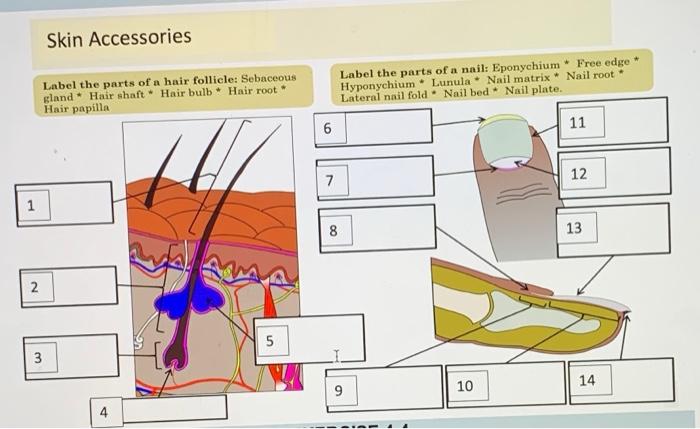



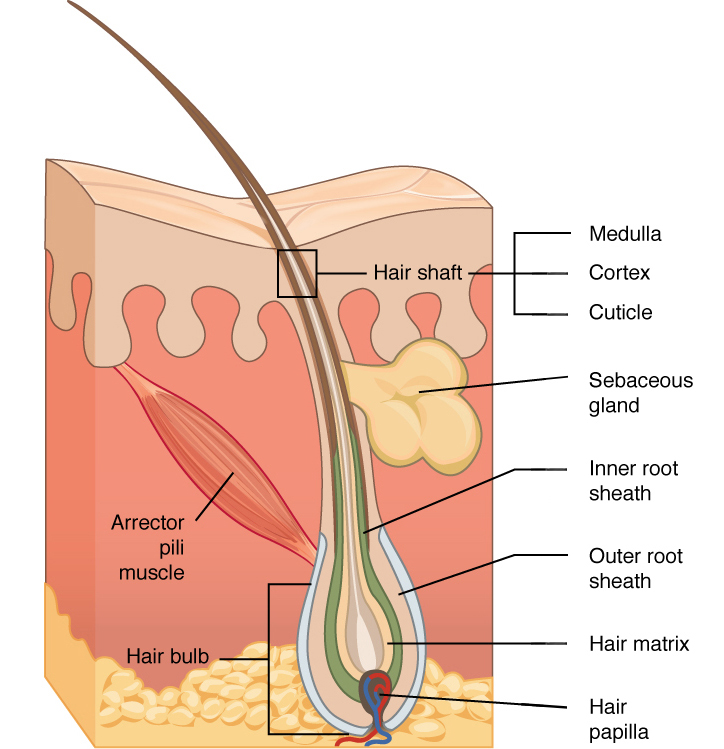
Solved Skin Accessories Label The Parts Of A Hair Follicle Chegg Com
Explain with well labelled diagram different regions of root and also explain structure of root hair?(iii) By what process do these substances enter the root hair ?Click Images to Large View Cross Section Of Zea Mays Corn Stem Showing Its Xylem Plant Anatomy Biology 121 With Matznerhall At Augustana Click Images to Large View Plant Anatomy Biology 121 With Matznerhall At Augustana Eisco Zea Mays Root Tip Cross Section 1 X 3 In 25 X 77 Click Images to Large View Eisco Zea Mays Root Tip Cross Section 1
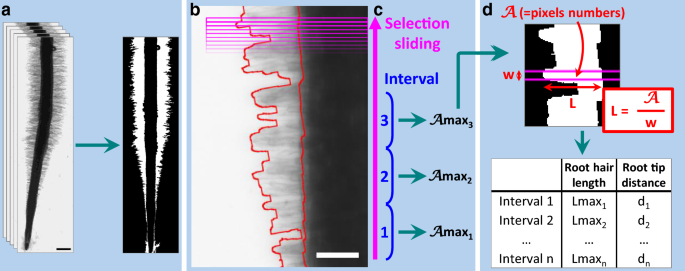



Root Hair Sizer An Algorithm For High Throughput Recovery Of Different Root Hair And Root Developmental Parameters Plant Methods Full Text




Ve Ds E Ele 4 The Diagram Alongside Represents A Layer Of Epidermal Cells Showing A Fully Grown Root Hair Study The Diagram And Answer The Questions That Follow A Name The
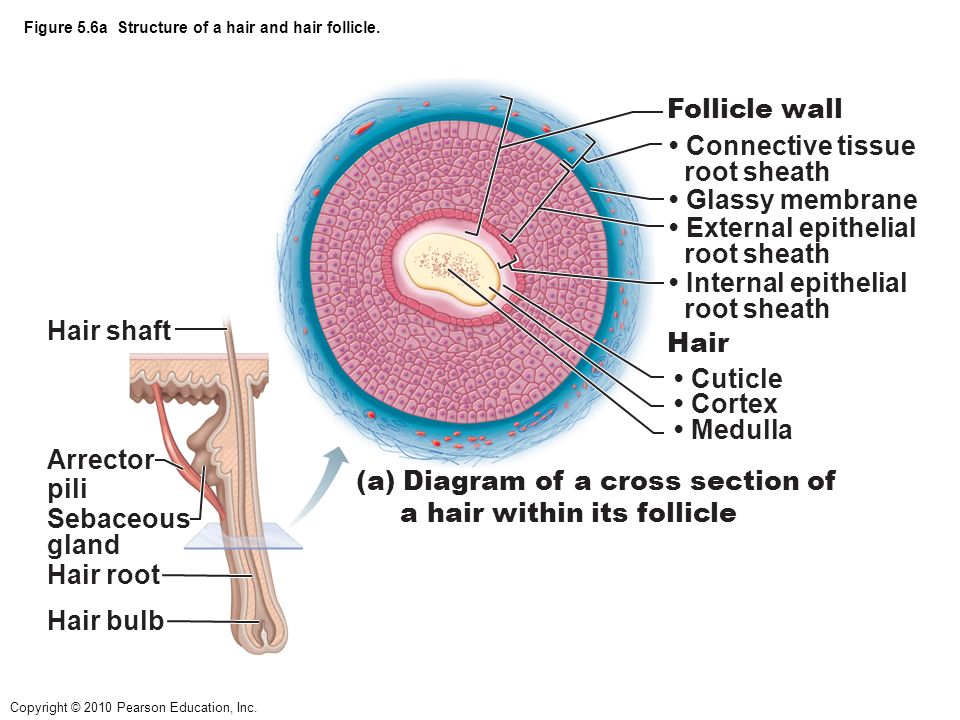
Skin Tissue Hair follicle Cells and connective tissue that surrounds the root of the hair Arrector Pili Can you identify the skin structures in the diagram?Test your knowledge on this science quiz to see how you do and compare your score to Basic hair structure explained Learn how all parts of the hair shaft function ( cuticle, medulla and cortex layers) using the hair shaft and hairA hair follicle anchors each hair into the skin The hair bulb forms the base of the hair follicle In the hair bulb, living cells divide and grow to build the hair shaft Blood vessels nourish
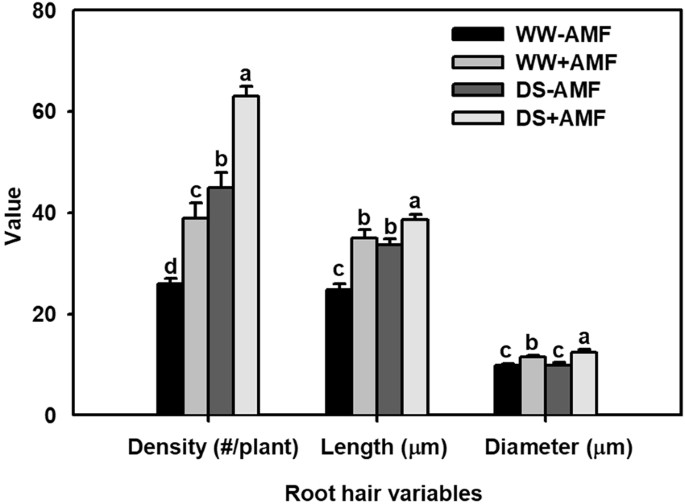



Mycorrhiza Stimulates Root Hair Growth And Iaa Synthesis And Transport In Trifoliate Orange Under Drought Stress Scientific Reports



Red Blood Cell
Define adventitious roots Describe the cells of the region of meristematic activity of the root Name the two plants which have stilt roots developing from the nodes of their stems What are the lateral roots of the primary root called?Explain the structure of root hair with the help of neat and labelled diagrams Advertisement Remove all ads Solution Show Solution 1 Root hair is a cytoplasmic extension (prolongation) of epiblema cell 2 Each root hair may be approximately 1 to 10 mm long and tubelike structure 3 It is colourless, unbranched, shortlived (ephemeral), and very delicate 4 It has a large central•Accessory organs include the hair (hair root and hair shaft) , hair follicle , pili arrector muscle, sebaceous gland , sudoriferous gland , nails , and mammary gland ebneshahidi ebneshahidi Functions of the Integumentary system 1 protection a) chemical factors in the skin Sebum (or oil) from the sebaceous glands is slightly acidic, retarding bacterial colonization on the skin surface




Hair And Nails Anatomy And Physiology I




18 Root Hair Cell Illustrations Clip Art Istock
Options (A), (B), and (D) are incorrect because in the above diagram the structure labeled as P at the extreme corner represents the nucleus of the root hair cell The structure labeled as Q which is a large structure in the root hair cell covering most of its area represents the vacuole of the root hair cell, and the structure labeled as R represents the cell wall of the root hair cell that Yes, your hair is much more than just a long, tiny threadlike structure that adds to your look Understanding hair anatomy is as crucial as learning about a healthy diet Especially because the human scalp contains on average between 80,000 and 100,000 hairs according to Healthline Hair is the characteristic feature of all mammals, and it has(iv) What will happen to the root hair if some fertilizer is added to the soil near the root hair?




Pin On Stock Photos For Sale Online




Drawing Shows How Hair Follicle Was Divided Into Three Parts Download Scientific Diagram
The diagram B is the root hair of an aquatic plant (i) Name the parts 1,2,3 (ii) Name two substances which enter the root hair What are their uses ?The diagram shows a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair Answer the questions by seeing the diagram (i) Name the parts labelled A B, C and D (ii) The root hair cell is in a turgid state Name and explain the process which caused this state (iii) Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B (iv) Draw a diagram of the above root hair cell asHair also has a sensory function due to sensory innervation by a hair root plexus surrounding the base of each hair follicle Hair is extremely sensitive to air movement or other disturbances in the environment, much more so than the skin surface This feature is also useful for the detection of the presence of insects or other potentially damaging substances on the skin surface Each hair



Roots Stems And Leaves Diagrams



2
Facts about Root Hair Cells explain about the rhizoid of a vascular plant People also call it as absorbent hair The epidermis of the plant root features this hairforming cell You can use the naked eyes to see the root hair cells There is no need for you to spot it under the microscopes You will not spot the root hair cells all over the root They are concentrated on the area where2D Diagram of the Root Hair Cell Cytoplasm is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane Nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell and contains DNA Cell Wall is a tough and flexible wall that surrounds some types of cells and provide cells with structural support and protection Cell Membrane is the semipermeable membrane surroundingAdvertisement Remove all ads Solution Show Solution (i) 1 Nucleus 2 Vacuole 3 Cell wall 4 Cell membrane (ii) Part 4 is the cell membrane It is semi




Water Movement In Flowering Plants Edexcel Igcse Biology Revision Notes
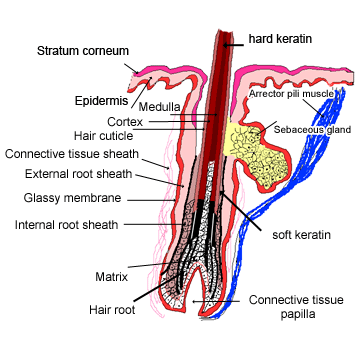



Skin The Histology Guide
(iv) Account for the different shapes of root hairs in the two diagrams Answer (i) 1Nucleus 2Cell wall 3Cytoplasm of the root hair cell (ii) 1 Water Anatomy of the Root of both Dicot and Monocot Plants The roots are a very important organ in plants They develop from the radicle and help in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil that is required for the plant life The roots fix the plant to the ground and provide support to the part of theHuman Skin Anatomy vector illustration of diagram of human skin anatomy root hair stock illustrations Deep Faith a conceptual illustration of a firmly rooted faith root hair stock illustrations Plant Root Close up of a plant roots taken out of the soil root hair stock pictures, royaltyfree photos & images The structure of the hair root and the sebum This is the structure of the hair root



Support And Transport In Plants Presentation Plants Animals And Ecosystems




Biology Root Hair Cell Diagram Diagram Quizlet
Root hair, or absorbent hairs, are tubular outgrowths of an epidermal cell of a root, a hairforming cell on the epidermis of a plant rootThese structures are lateral extensions of a single cell and are only rarely branched They are found in the region of maturation, also called the zone of differentiation of the root Just prior to and during root hair cell development, there is elevatedRoots, Stems and Leaves Diagrams External Root Structure Monocot Root Dicot Root External Structure of a Woody Stem Monocot Stem Woody Dicot Stem Monocot Leaf Dicot Leaf The primary root then further divides to form the secondary root, tertiary root, and root hairs to complete the root system What Are the Main Parts of a Plant Root System A typical plant root system shows four distinct regions or zones 1) region of root cap , 2) region of cell division or meristematic region 3) region of elongation, and 4) region of maturation or



World Carrot Museum Description Of Carrot Root



2
(ii) Is the root hair cell unicellular or multicellular ?Draw one line from each root hair cell to the correct process Root hair cell Process (2) (Total 5 marks) Q2 The figure below shows a scale drawing of one type of cell in blood (a) Use the scale to determine the width of the cell GiveThis is extremely beneficial to plants that live in dry areas
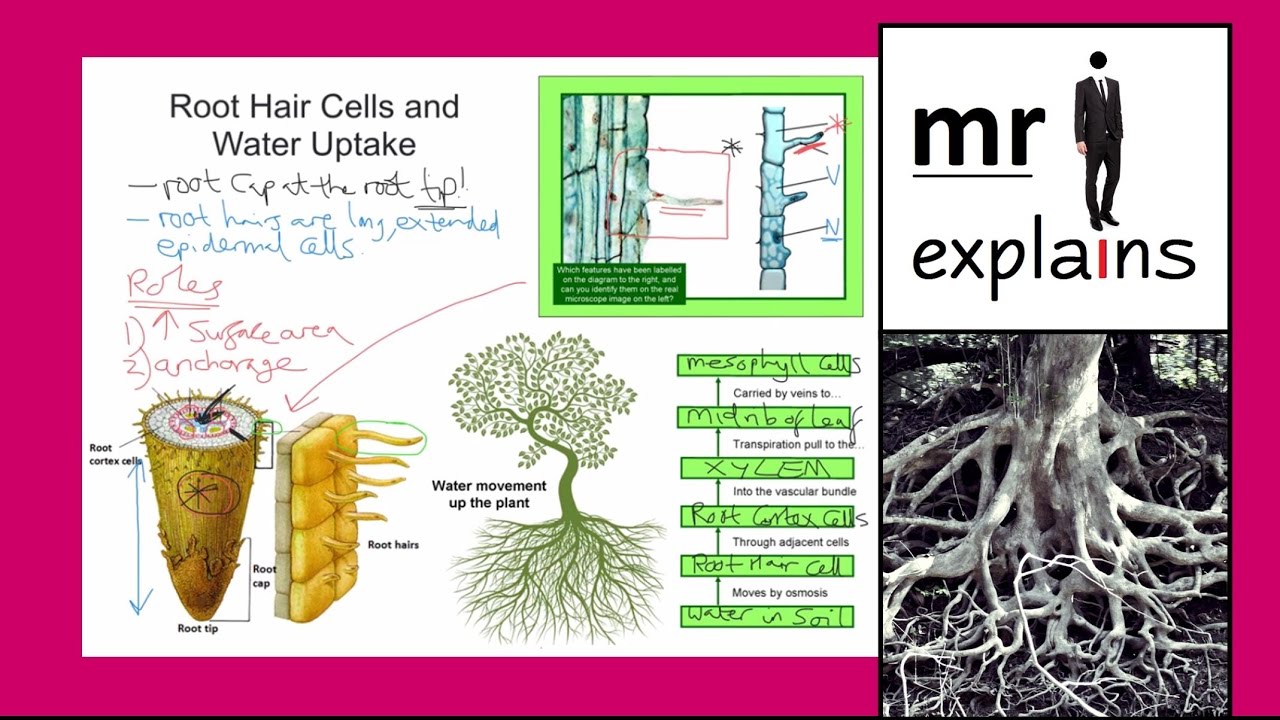



Mr I Explains Root Hair Cells And Water Uptake For Igcse Youtube




Human Anatomy Skin And Hair Diagram Stock Vector Image By C Matoommi
Medium Open in App Solution Verified by Toppr The root is normally an underground piece of the plant which helps in obsession and ingestion of water The root with its branches is known as the root framework Qualities of the Root (I) The root is the diving part of the plant pivot and is(iii) Why is the root hair onecelled?Water enters the root hair cells in the soil by osmosis This is a labelled diagram of a root hair cell The function of the root hair cell is to obtain water from the ground and transport this to the Xylem Plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis Root hair cells are adapted for this by having a large surface area to speed up osmosis




The Diagram Below Represents A Layer Of Epidermal Cells Knowledgeboat




Hair Under A Microscope Rs Science
The diagram shows some of the stages in IVF (in vitro fertilisation) Q12€€€€€€€€€ The drawing shows part of a root hair cell (a)€€€€ Use words from the list to label the parts of the root hair cell cell membrane €€€€€ cell wall €€€€€€€ cytoplasm €€€€€ nucleus €€€€€ vacuole (4) Page 16 of 27 (b)€€€€ TheThe diagrams show the concentration of different substances inside and outside a root hair cell How would each substance move into the root hair cell? A root hair cell in a plant absorbs minerals that have been dissolved in water They allow a plant to absorb these minerals by increasing the surface area;



2




Live Cell Profiles Of Immunolabeled Root Hairs A Lm10 Labeling Of A Download Scientific Diagram
It bears root hairs Root hairs are tubular extensions of the outer walls of the epidermal cells The root hairs bearing cells are smaller cells than other cells A thin layer of cuticle is also present on some epidermal cells Root hairs increase the absorptive surface , of the epidermal cells A root hair starts its growth as a small papilla on the outer wall The nucleus and cytoplasmRoot hair cell collecting mineral nutrients and water from soil, biological labeled plant system diagram Illustration about agriculture, cell, plasmodesma, functionThe below figure shows a root hair (i) Label the parts 1 to 4 (ii) What is the role of part 4?



Hair Biology For Majors Ii



Fbi Forensic Science Communications July 04
Monocot and Dicot Roots Type # 2 Anatomy of Monocot Root Zea maysRoot It is circular in outline and reveals the following tissues (Fig 173) from outside within Epiblema 1 Singlelayered epiblema consists of barrel shaped or rounded cells 2 From some cells arise unicellular hair Cortex 3 It is welldeveloped, several cells deep




Forensics Forensics Project Part Ii Hair And Fiber Analysis



Draw A Well Labelled Diagram Of The Regions Of The Root Tip Biology Topperlearning Com Lxabhr2vv
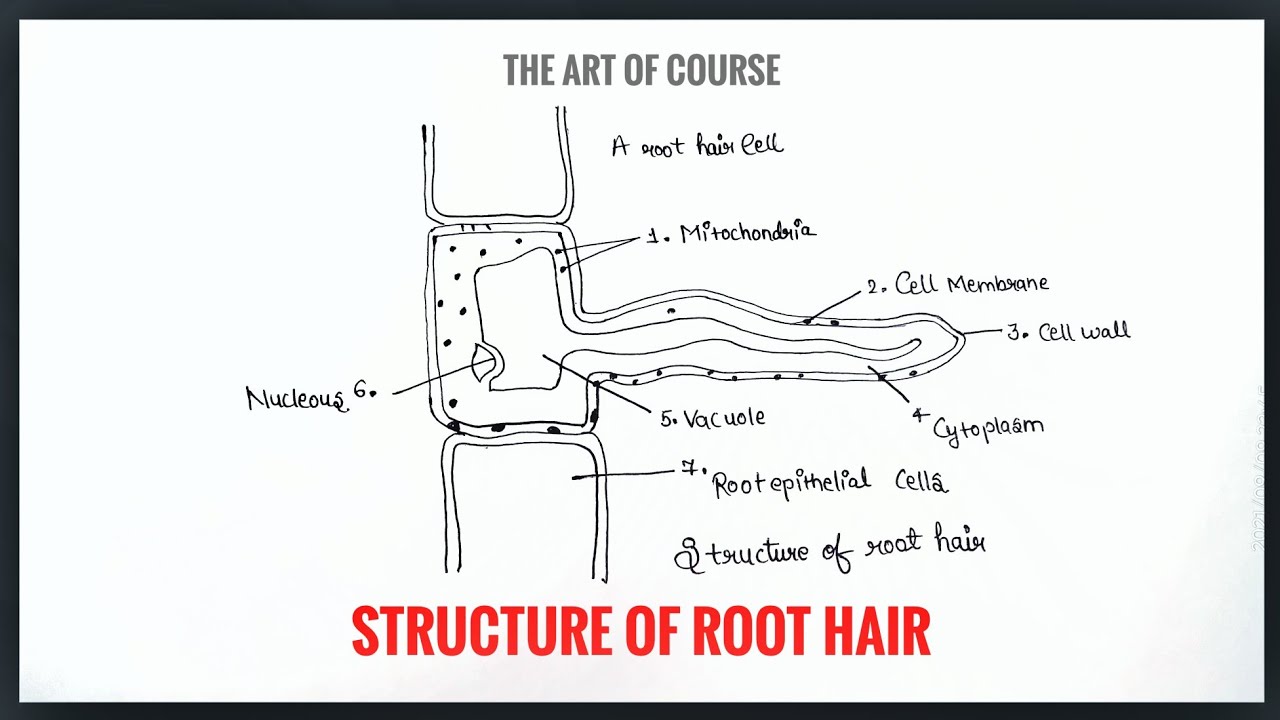



Structure Of Root Hair Diagram With Labelling Theartofcourse Youtube
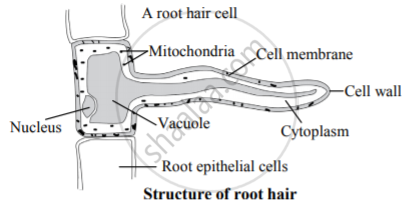



Draw A Neat And Labelled Diagram Of Root Hair Biology Shaalaa Com
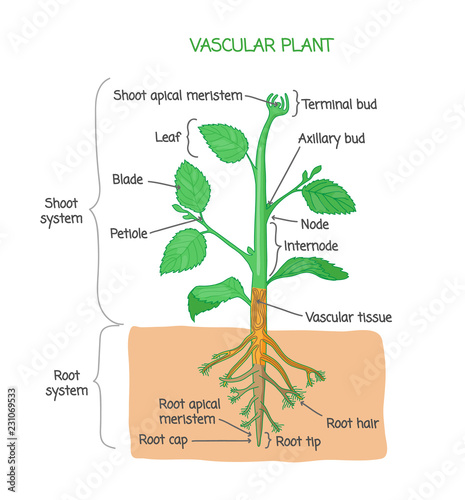



Vascular Plant Biological Structure Labeled Diagram Vector Illustration Stock Vector Adobe Stock



Plant Structures Roots Sparknotes
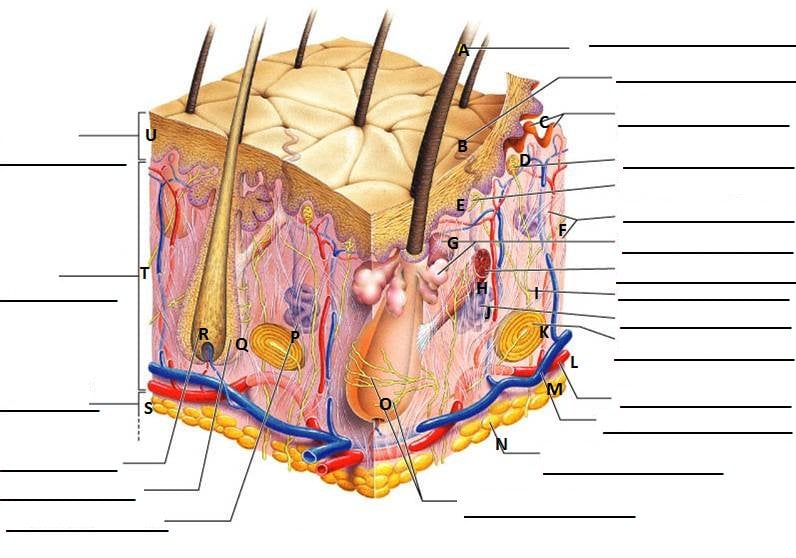



A Human Body Skin Structure Quiz Proprofs Quiz



Root Hairs



3
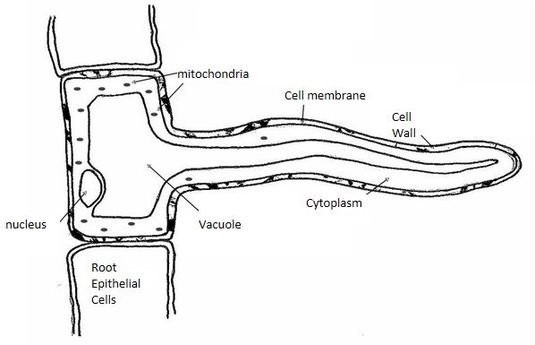



Table Of Organelles Root Hair Cell
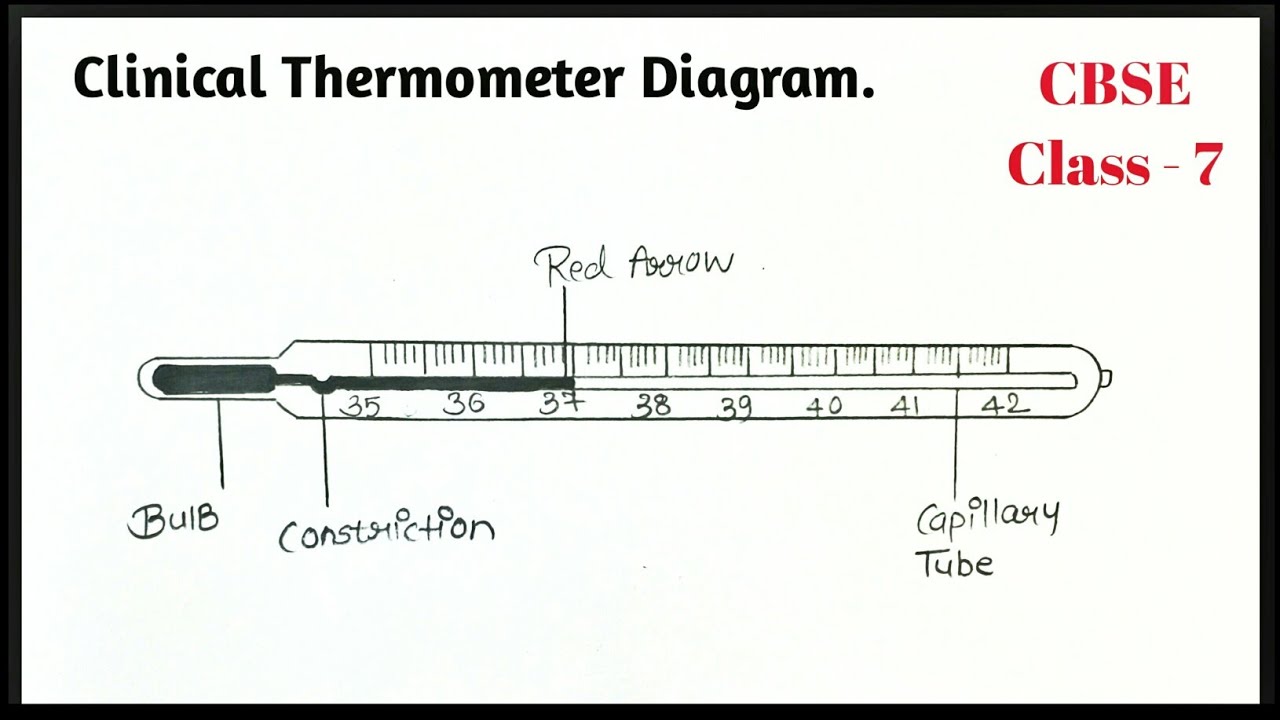



Structure Of Root Hair Diagram With Labelling Theartofcourse Youtube



The Below Figure Shows A Root Hair Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




The Diagram Below Represents A Layer Of Epidermal Cells Showing A Fully Grown Root Hair



What Is The Cellular Structure Of A Root Hair Cell Quora
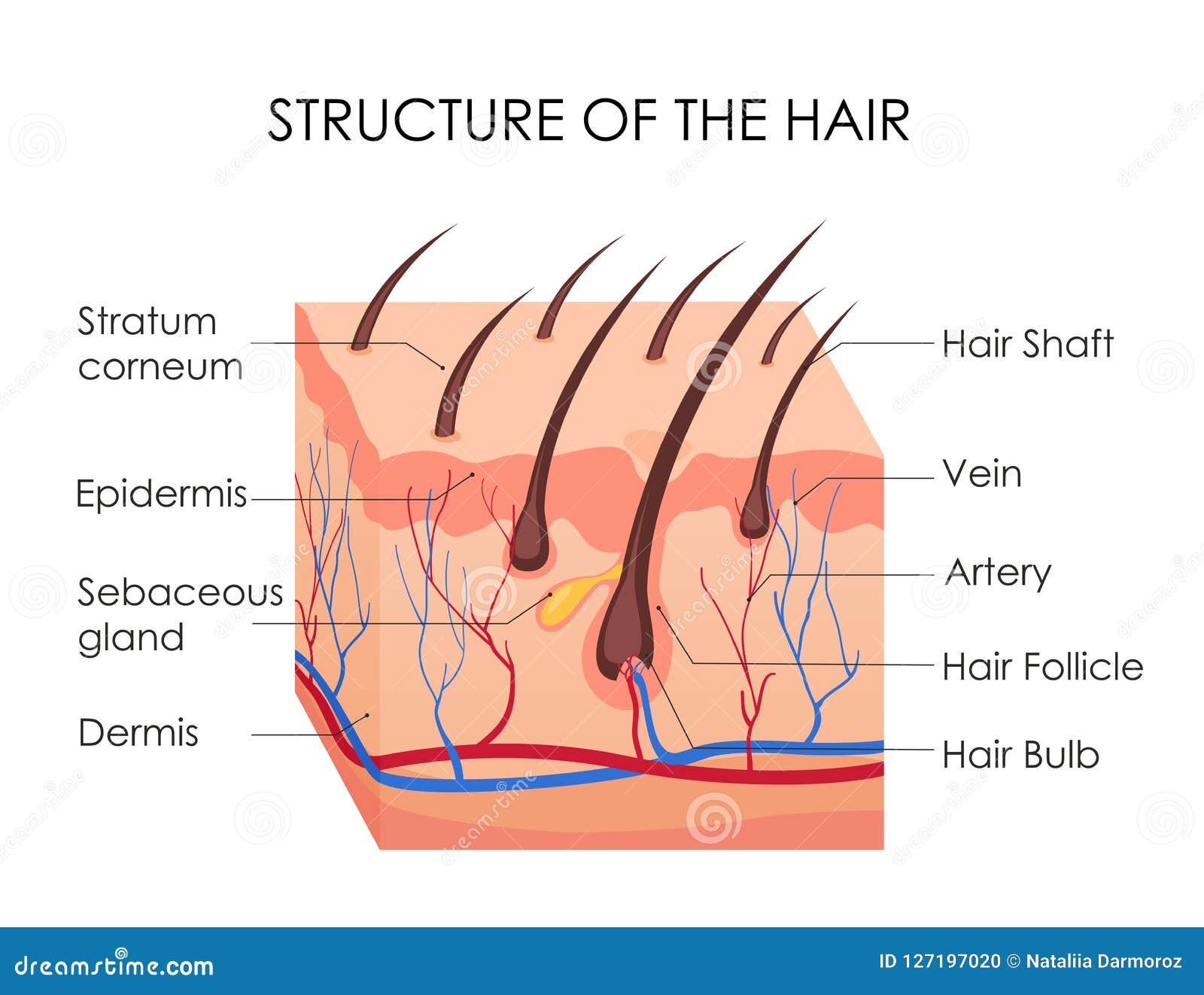



Hair Diagram Stock Illustrations 2 243 Hair Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
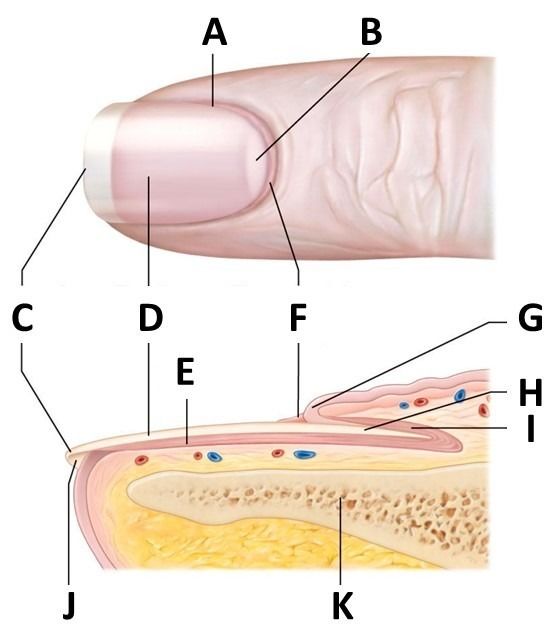



Nail And Structure Quiz




Explain The Way How Plants Get Water By Osmosis Through Root Hair Cbse Class 10 Learn Cbse Forum




Root Hair Cells Occurrence Dimensions Structure




Labeled Skin And Hair Anatomy Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock




Root Hair Cells Occurrence Dimensions Structure
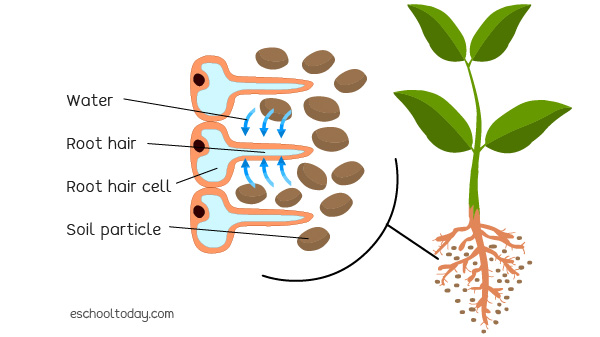



Structure Of The Root Hairs Eschooltoday



Draw A Magnified View Of The Root Hair And Describe How It Helps In The Absorption Of Water From The Soil Studyrankersonline




Live Cell Lm15 Labeling Of Wild Type Wt Arabidopsis Root Hairs A Download Scientific Diagram




Root Hair Cell Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
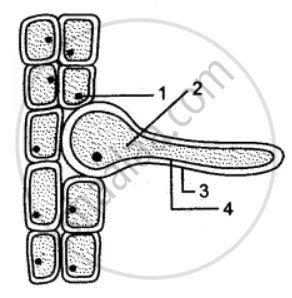



The Below Figure Shows A Root Hair I Label The Parts 1 To 4 Ii What Is The Role Of Part 4 Iii Why Is The Root Hair One Celled Iv What Will




Primary Root Tissue Root Hairs And The Plant Vascular Cylinder Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
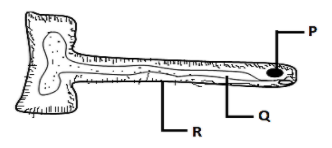



Identify The Parts Labeled P Q And R In The Diagram Class 11 Biology Cbse




Human Hair Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
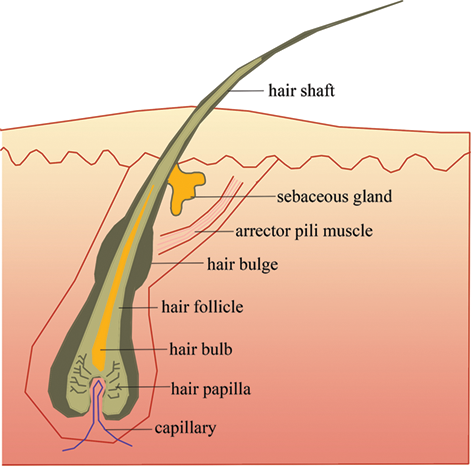



Anatomy And Physiology Of Hair Intechopen
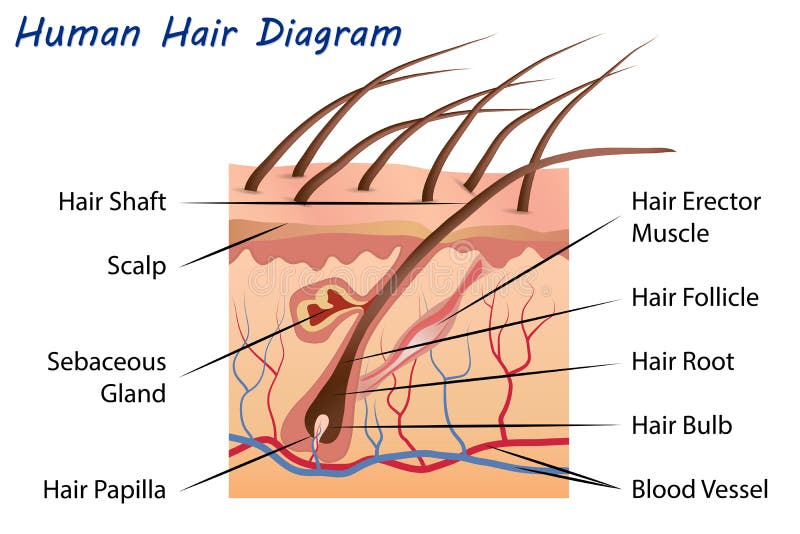



Human Hair Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Care




Label The Features Of The Hair Follicle Diagram Quizlet



1




Illustration Of Anatomy Of Hair With Label On White Background Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Hair Follicle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Long Answer Question Describe Structure Of Root Hair Biology Shaalaa Com




Labeled Skin And Hair Anatomy Detailed Medical Illustration Canvas Print Barewalls Posters Prints Bwc



The Diagram Below Represents A Layer Of Epidermal Cells Showing A Fully Grown Root Hair Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Art Labeling Activities




Adaptations Of Specialised Cells Bio Journal Anna Ying



Root Hair Cell Transport In Flowering Plants
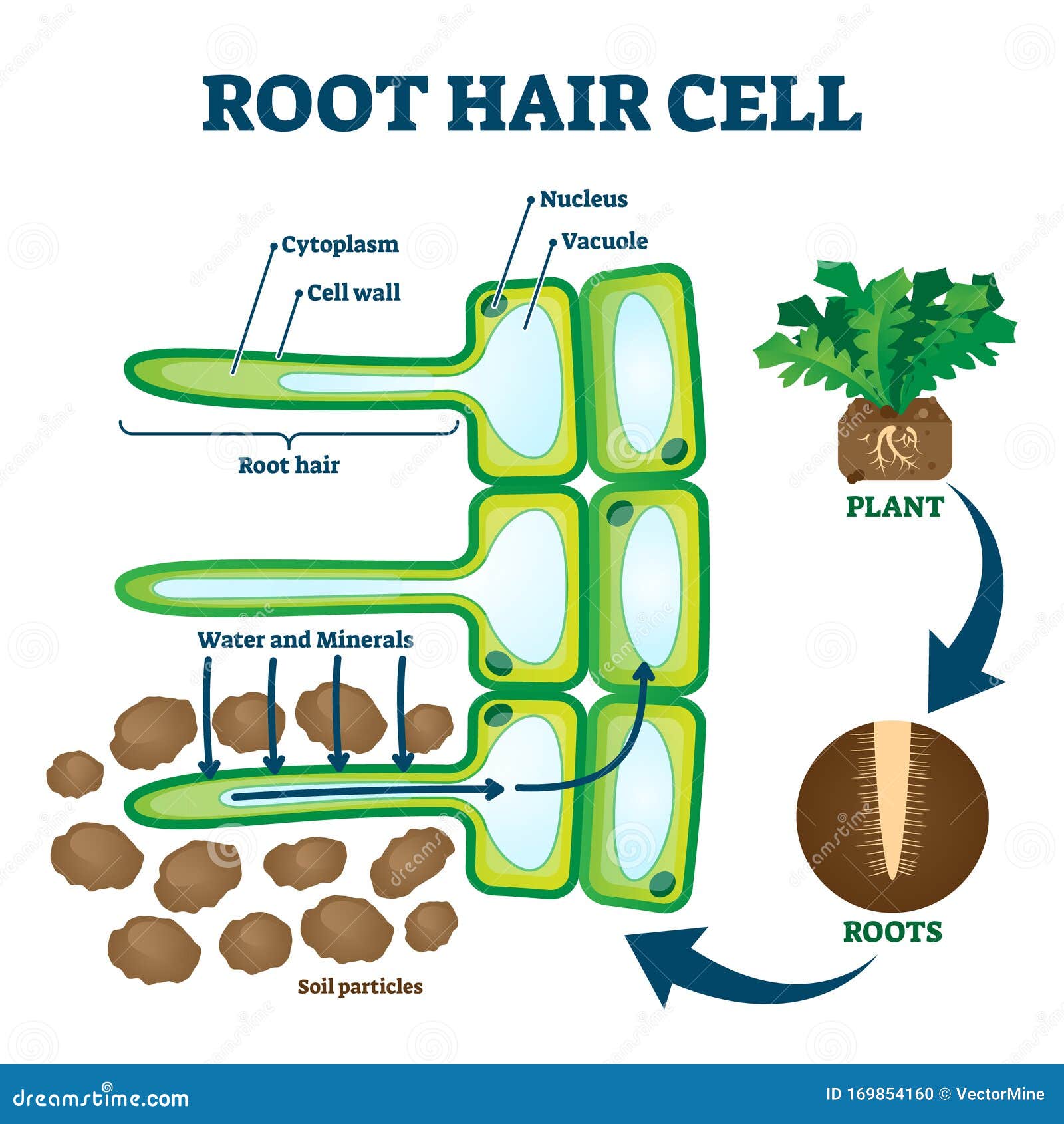



Root Hair Cell Collecting Mineral Nutrients And Water From Soil Biological Labeled Plant System Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Agriculture Cell




The Figure Given Below Is A Diagrammatic Representation Of A Part Of The Cross Section Of The Root In The Root Hair Zone




Skin 2 Accessory Structures Of The Skin And Their Functions Nursing Times
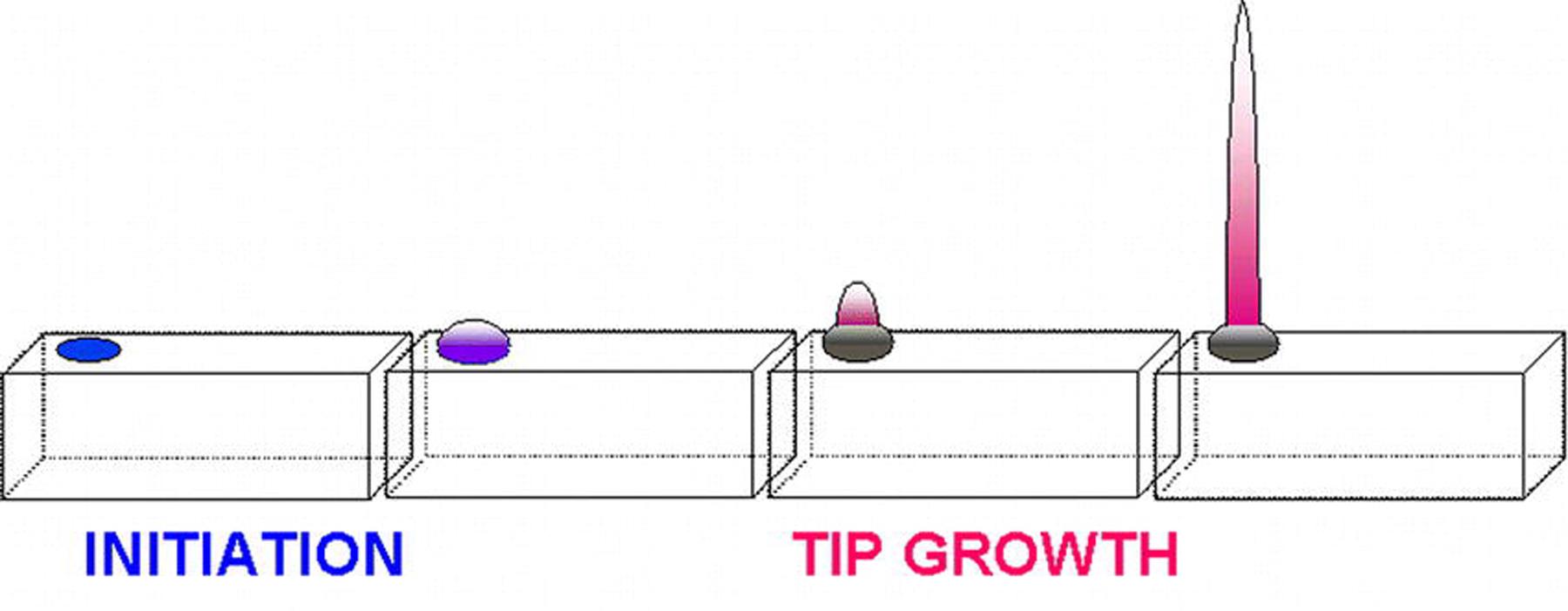



Root Hairs




Q1 Draw A Magnified View Of Th Lido



Root Hair
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/hair-shaft/6LDs0jBCUnUduhXT7SCGw_Hair_shaft_02.png)



Integumentary System Definition Diagram And Function Kenhub



2



2
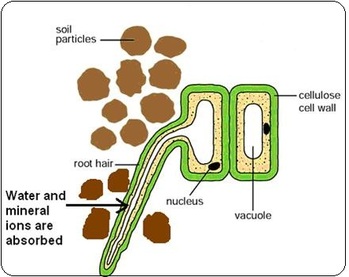



Active Transport Biology Notes For Igcse 14




Labeled Hair Follicle Diagram Labeled Hair Follicle Diagram Layers Of The Skin Skin Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology Integumentary System




Root Hair Cells Adaptations Teaching Resources




Hair Follicle Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Hair Follicle Receptor Root Hair Plexus Adipose Tissue Ppt Video Online Download




Draw A Labelled Diagram Of The Root Hair Cell As It Would Appear If Some Fertilizer Is Added To The Brainly In




Hair Labeling Diagram Quizlet




1 The Diagram Below Represents A Layer Of Epidermalcells Showing A Fully Grown Root Hair Study Brainly In




Structure And Composition Of The Hair




Human Hair Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Diagram Below Represents A Layer Of Epidermal Cells Knowledgeboat




Cell Specialisation Aqa Gcse Biology Revision Notes



Draw A Diagram Of Magnified Root Hair Biology Topperlearning Com Qvu9mxthh
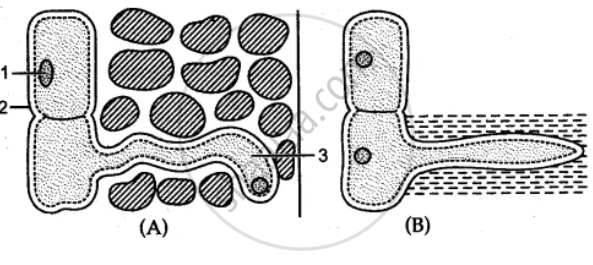



The Alongside Diagram A Shows A Root Hair Growing Through The Soil Particles Diagram B Is The Root Hair Of An Aquatic Plant Biology Shaalaa Com




Plant Structure Gcse Biology Edexcel Revision Study Rocket
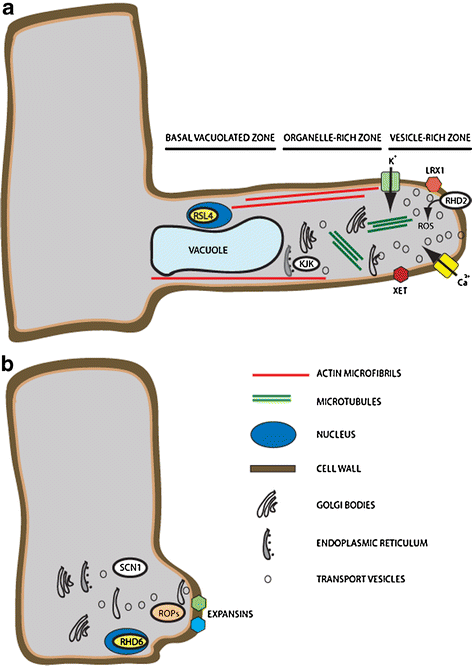



Root Hairs Development Growth And Evolution At The Plant Soil Interface Springerlink
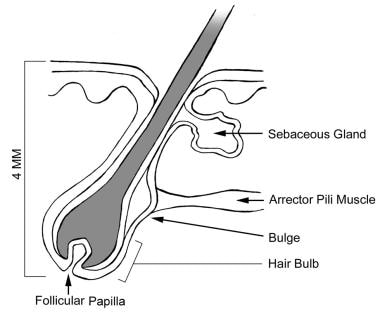



Hair Anatomy Overview Microanatomy Of Anagen Phase Hair Microanatomy Of Catagen Phase Hair




Explain With Well Labelled Diagram Different Regions Of Root And Also Explain Structure Of Root Hair




Identify The Parts Labelled P Q And R In The Diagram Of A Root Hair Cell Shown



2




Human Body Skin Anatomy Diagram Infographic Chart Figure With All Parts Hair Sweat Gland Artery Vein Supply Blood Vessel Canstock




5 5 Uptake Of Water And Minerals In The Roots Support And Transport Systems In Plants Siyavula



Plant Structures Roots Sparknotes
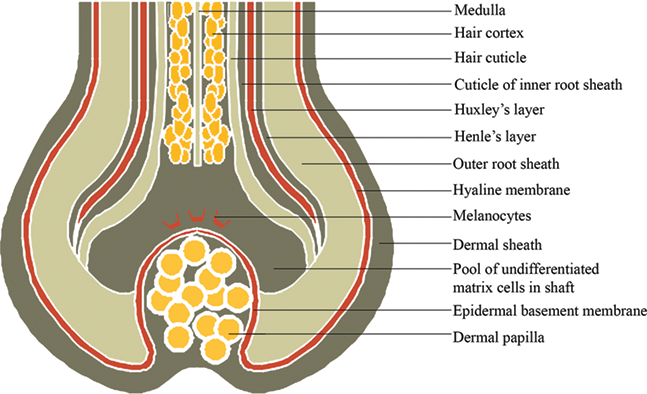



Anatomy And Physiology Of Hair Intechopen




Pin By Charmayne Walker On Natural Hair Care And Styles Natural Hair Styles Balayage Hair Hair Facts
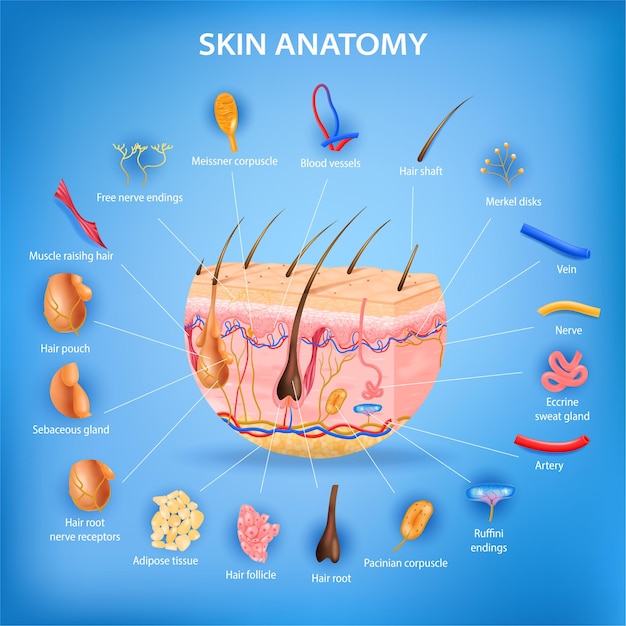



Free Vector Skin Anatomy Realistic Poster With Layers And Labeled Parts Illustration




5 5 Uptake Of Water And Minerals In The Roots Support And Transport Systems In Plants Siyavula
コメント
コメントを投稿